Use Case: Configuring an Elastic Virtual Switch for a Tenant
Objective – This use case shows how to set up an elastic virtual switch (HR) across two compute nodes for a tenant.
In this use case, you connect the VNIC vnic0 on CN1 and the VNIC anet of the zone z1 to the elastic virtual switch HR, so that they are a part of the same L2 segment and they can communicate with each other on a VXLAN. The VNICs are part of the tenant tenantA. The following figure shows the EVS setup.
Figure 6-3 Elastic Virtual Switch Configuration for a Tenant
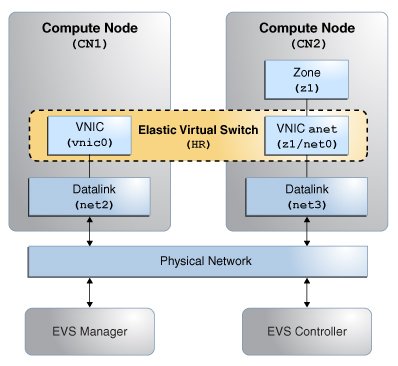
The figure shows a network with four nodes that contains the following components:
-
Two compute nodes (CN1 and CN2)
-
Zone z1 on CN2 with a VNIC anet resource
-
VNIC vnic0 on CN1
-
A node that acts as an EVS controller, CONTROLLER
-
A node that acts as an EVS manager on which you need to run the evsadm command, MANAGER
-
A VXLAN to implement the elastic virtual switch HR
-
uplink-port that specifies the datalink that is used for the VXLANs
Planning for the Elastic Virtual Switch Setup
-
Install the mandatory EVS packages. For information about the required packages, see Mandatory Packages for Using EVS.
Note - The evsuser is a specific user that is created when you install the pkg:/service/network/evs package. The user, evsuser, is assigned with the Elastic Virtual Switch Administration rights profile. This profile provides all the required authorizations and privileges to perform EVS operations. -
Set up SSH authentication with the preshared public key for evsuser between the following components in the EVS setup:
-
The EVS manager and the EVS controller
-
Each EVS node and the EVS controller
-
The EVS controller and each EVS node
For more information, see Setting Up SSH Authentication.
Note - This use case assumes that the controller property is set to ssh://[email protected] on each of the EVS node, EVS manager, and EVS Controller. -
-
Configure the EVS controller and set the controller properties.
-
Set the EVS controller on all the compute nodes and then set the controller properties that specify how to implement the elastic virtual switch across the compute nodes.
-
Specify the properties l2-type, vxlan-range, and uplink-port. Otherwise, you cannot create the elastic virtual switch.
-
-
Create an elastic virtual switch. You must associate an IPnet and add a VPort to the elastic virtual switch.
-
Create a temporary VNIC on CN1 and connect the VNIC to the VPort of the elastic virtual switch.
-
Create a VNIC anet on the zone z1 and connect the VNIC anet resource to the elastic virtual switch.
EVS Manager Operations
-
Set the EVS controller.
MANAGER# evsadm set-prop -p controller=ssh://[email protected]
-
Set the EVS controller properties.
-
Set the type of L2 topology that must be used for the elastic virtual switch. This example uses a VXLAN.
MANAGER# evsadm set-controlprop -p l2-type=vxlan
-
Set the VXLAN range.
MANAGER# evsadm set-controlprop -p vxlan-range=200-300
-
Specify the datalinks (uplink-port) that are used for the VXLAN.
MANAGER# evsadm set-controlprop -p uplink-port=net2
MANAGER# evsadm set-controlprop -h CN2 -p uplink-port=net3
Note - You can configure the controller from any node in the data center as long as you can connect to the EVS controller and have the required authorizations. For more information, see Security Requirements for Using EVS. -
-
Verify the EVS controller properties.
MANAGER# evsadm show-controlprop -p l2-type,vxlan-range,uplink-port NAME VALUE DEFAULT HOST l2-type vxlan vlan -- vxlan-range 200-300 -- -- uplink-port net2 -- -- uplink-port net3 -- CN2
-
Create the elastic virtual switch HR for the tenant tenantA.
MANAGER# evsadm create-evs -T tenantA HR
-
Add the IPnet hr_ipnet to the elastic virtual switch HR.
MANAGER# evsadm add-ipnet -T tenantA -p subnet=192.168.100.0/24 HR/hr_ipnet
-
Add the VPort vport0 to the elastic virtual switch HR.
MANAGER# evsadm add-vport -T tenantA HR/vport0
-
Verify the elastic virtual switch that was created for the tenant tenantA.
MANAGER# evsadm NAME TENANT STATUS VNIC IP HOST HR tenantA -- -- hr_ipnet -- vport0 -- free -- 192.168.100.2/24 --
-
Check the MAC address and the IP address associated with HR/vport0.
MANAGER# evsadm show-vportprop -p macaddr,ipaddr HR/vport0 NAME TENANT PROPERTY PERM VALUE DEFAULT POSSIBLE HR/vport0 tenantA ipaddr r- 192.168.100.2/24 -- -- HR/vport0 tenantA macaddr r- 2:8:20:d8:da:10 -- --
-
Check the VXLAN segment ID associated with the elastic virtual switch HR.
MANAGER# evsadm show-evs -L EVS TENANT VID VNI HR tenantA -- 200
Compute Node CN1 Operations
-
Specify the EVS controller.
CN1# evsadm set-prop -p controller=ssh://[email protected]
-
Create a temporary VNIC vnic0 and connect it to the elastic virtual switch HR/vport0.
CN1# dladm create-vnic -t -T tenantA -c HR/vport0 vnic0
-
Verify the VNIC that was created.
CN1# dladm show-vnic -c LINK TENANT EVS VPORT OVER MACADDRESS VIDS vnic0 tenantA HR vport0 evs-vxlan200 2:8:20:d8:da:10 0
The MAC address of vnic0 maps to the MAC address of the VPort.
-
Check the allowed IP addresses for vnic0.
CN1# dladm show-linkprop -p allowed-ips vnic0 LINK PROPERTY VALUE EFFECTIVE DEFAULT POSSIBLE vnic0 allowed-ips 192.168.100.2 192.168.100.2 -- --
The allowed-ips property is set to the IP address associated with the VPort. This output means that you cannot create any IP address on vnic0 other than 192.168.100.2.
-
Create an IP interface for vnic0 and assign 192.168.100.2 as the IP address.
# ipadm create-ip -t vnic0 # ipadm create-addr -t -a 192.168.100.2 vnic0
-
Check the automatically generated VXLAN datalink.
CN1# dladm show-vxlan LINK ADDR VNI MGROUP evs-vxlan200 0.0.0.0 200 224.0.0.1
Compute Node CN2 Operations
-
Specify the EVS controller.
CN2# evsadm set-prop -p controller=ssh://[email protected]
-
Configure the VNIC anet for the zone z1 and connect it to the elastic virtual switch.
CN2# zonecfg -z z1 Use 'create' to begin configuring a new zone zonecfg:z1> create create: Using system default template 'SYSdefault' zonecfg:z1> set zonepath=/export/zones/z1 zonecfg:z1> set tenant=tenantA zonecfg:z1> select anet linkname=net0 zonecfg:z1:anet> set evs=HR zonecfg:z1:anet> end zonecfg:z1> commit zonecfg:z1> exit
-
Install and boot the zone z1.
CN2# zoneadm -z z1 install CN2# zoneadm -z z1 boot
-
Log in to the zone z1 and complete the zone configuration.
CN2# zlogin -C z1
For more information about zone configuration, see Creating and Using Oracle Solaris Zones .
-
Verify the VNIC anet resource that was created.
CN2# dladm show-vnic -c LINK TENANT EVS VPORT OVER MACADDRESS VIDS z1/net0 tenantA HR sys-vport0 evs-vxlan200 2:8:20:1a:c1:e4 0
Because the VPort is not specified, the EVS controller creates a system VPort sys-vport0 for the VNIC anet resource.
-
Display the information that is related to the VPort.
CN2# evsadm show-vport -o all NAME TENANT STATUS VNIC HOST MACADDR IPADDR HR/sys-vport0 tenantA used z1/net0 CN2 2:8:20:1a:c1:e4 192.168.100.3/24
The VNIC anet resource is plumbed and assigned the VPort's IP address.
-
Verify the IP address of the VNIC anet z1/net0.
CN2# zlogin z1 ipadm NAME CLASS/TYPE STATE UNDER ADDR lo0 loopback ok -- -- lo0/v4 static ok -- 127.0.0.1/8 lo0/v6 static ok -- ::1/128 net0 ip ok -- -- net0/v4 inherited ok -- 192.168.100.3/24